Travel Notes: Africa - Somalia Travel Notes.
Short URL: https://tnot.es/SO
Somalia Travel and Tourism on Travel Notes
The current travel advisories for Somalia strongly advise against all but essential travel due to the high risk of terrorism, kidnapping, piracy, and civil unrest.
About Somalia
Somalia has a high risk of terrorism, crime, civil unrest, kidnapping, and health issues, so most countries have issued a travel advisory warning against all travel to the country.
Despite this, some parts of the country, such as Somaliland, have seen a rise in tourism in recent years due to political stability and improving infrastructure.
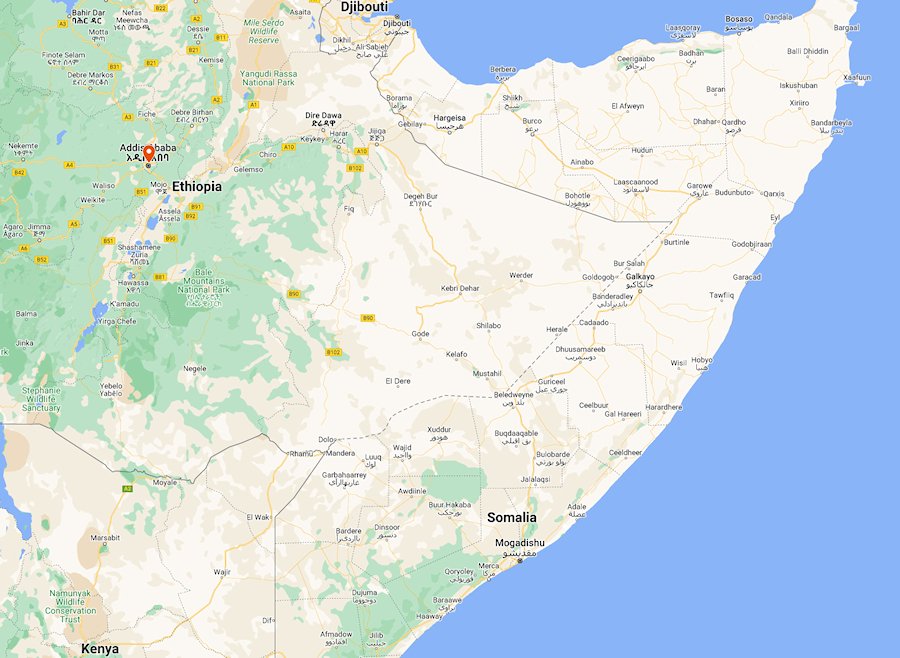
Countries neighbouring Somalia: Kenya, Ethiopia and Djibouti.
 Add a Business - Add a Location -
Add a Lodging - Add Travel Content
- Add URL
- Travel Services.
Add a Business - Add a Location -
Add a Lodging - Add Travel Content
- Add URL
- Travel Services.
Mapping Somalia
Map of Somalia
The Somali Democratic Republic has a long coastline; effectively two. In the north is the Gulf of Aden, and in the east and south the Indian Ocean.
Somalia Overview
Somalia is a country located in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the north-west, the Gulf of Aden to the north, the Indian Ocean to the east, and Kenya to the south-west.
Somalia continues to strive for stability and development, albeit facing significant obstacles along the way.
Despite its challenges, Somalia retains cultural vibrancy and resilience, with a rich heritage of poetry, music, and traditional art forms.
Civil War and Conflict
Following the overthrow of President Siad Barre in 1991, Somalia descended into a prolonged period of civil war and anarchy.
Various factions, warlords, and clan-based militias vied for power, leading to widespread violence, displacement, and humanitarian crises.
The absence of a functioning central government led to the emergence of autonomous regions, such as Somaliland and Puntland.
Economy
Somalia's economy is primarily agrarian, with livestock being a major export.
Additionally, remittances from the Somali diaspora play a significant role in the economy.
Despite having potential resources such as fisheries and minerals, the country's economy has been severely impacted by decades of conflict and instability.
Geography
Somalia has a diverse landscape, including arid plains, plateaus, highlands, and coastal regions.
The Juba and Shabelle rivers are the main sources of water in the country.
Somalia experiences a predominantly dry climate with periodic droughts.
History
Somalia has a rich history, with ancient trading civilisations like the Sultanate of Adal and the Ajuran Empire.
In the late 19th century, it was colonised by European powers.
Italy controlled the southern part (Italian Somaliland) while Britain controlled the north (British Somaliland).
The two regions united in 1960 to form the independent Republic of Somalia.
Piracy
Somalia gained international notoriety in the early 21st century due to piracy off its coast, particularly in the Gulf of Aden and the Indian Ocean.
Somali pirates hijacked commercial vessels, leading to significant disruption of international maritime trade.
International naval patrols and increased security measures have since reduced piracy activities; although the underlying issues, such as poverty and instability, persist.
Political Situation
Somalia has been undergoing a process of reconstruction and stabilisation.
The Federal Government of Somalia, established in 2012, has been working to restore security and governance, with the support of the international community.
However, challenges such as political infighting, corruption, and ongoing insurgency by Al-Shabaab hinder progress.
Somali Language
The official languages of Somalia are Somali and Arabic, although English and Italian are also used.
Terrorism
Somalia has also been plagued by terrorism, with the emergence of groups like Al-Shabaab, an Islamist militant organisation affiliated with Al-Qaeda.
Al-Shabaab has conducted numerous attacks within Somalia as well as in neighbouring countries like Kenya.
The group aims to overthrow the Somali government and establish its version of Islamic rule.
Visiting Somalia
Travelling to Somalia is not recommended for most individuals due to ongoing security concerns, including the threat of terrorism, piracy, and violent crime.
The country has experienced significant instability, political unrest, and conflict for many years, making it a dangerous destination for tourists.
The U.S. Department of State and many other governments typically issue travel advisories advising against all travel to Somalia due to the high level of risk.
Kidnappings, armed conflict, and terrorist attacks are frequent occurrences in various parts of the country. Additionally, the lack of effective law enforcement and infrastructure further exacerbates the risks for travellers.
If you have specific reasons for considering travel to Somalia, such as essential business or humanitarian work, it's crucial to conduct thorough research, seek guidance from relevant authorities, and take necessary security precautions.
However, for most people, it's advisable to avoid travelling to Somalia altogether and consider alternative destinations with safer conditions.
Somalia Safety Concerns
Somalia has experienced significant security challenges due to ongoing conflict, terrorism, and piracy.
Certain areas, especially in the south-central regions, remain unsafe for travel due to the presence of militant groups like Al-Shabaab.
It's important to approach travel to Somalia with caution and thorough preparation due to the security risks.
Before considering a visit, it's crucial to research the current security situation and adhere to travel advisories issued by your government or reputable sources.
Consulting with local authorities and experienced travellers, as well as obtaining comprehensive travel insurance, can help mitigate potential challenges during your visit.
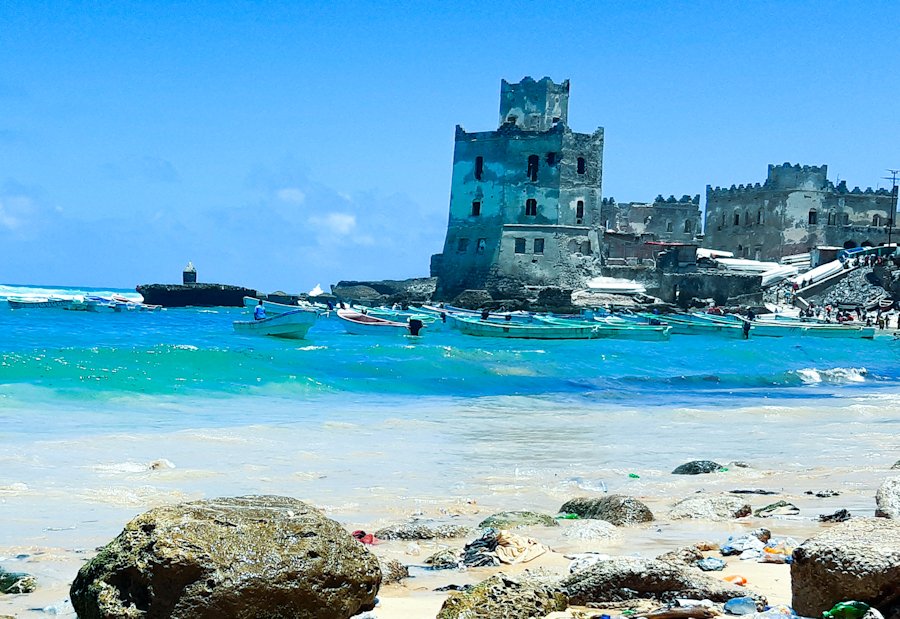
Beaches and Coastal Attractions
Somalia has a long coastline along the Indian Ocean, offering pristine beaches and opportunities for water-based activities like swimming, snorkelling, and diving.
Places like Mogadishu's Lido Beach and Jazeera Beach are popular among locals and visitors alike for relaxation and recreation.
Cuisine
Somali cuisine is characterised by its use of aromatic spices, grilled meats, and flavourful rice dishes.
You might sample traditional dishes like 'xalwo' (a sweet dessert), 'sambusa' (similar to samosas), or 'suugo suqaar' (a spicy meat stew served with rice or pasta).
Somali tea, often brewed with spices like cardamom and cinnamon, is a popular beverage enjoyed throughout the country.
Cultural Heritage
Somalia boasts a rich cultural heritage with influences from Arab, Islamic, and African traditions.
You might explore historical sites such as the ancient port city of Zeila, which has remnants of ancient civilisations and medieval Islamic architecture.
Additionally, Somali culture is renowned for its poetry, music, and traditional dance forms, providing opportunities to immerse yourself in the local arts scene.
Hospitality
Somalis are known for their hospitality and warmth towards guests.
You may have the opportunity to engage with locals, learn about their customs and traditions, and experience the famed Somali hospitality firsthand.
Wildlife and Nature
Despite the challenges, Somalia is home to diverse ecosystems and wildlife.
National parks and reserves like the Kismayo National Park provide opportunities for wildlife viewing, including species like elephants, giraffes, and various bird species.
Exploring Somalia's natural
landscapes, including mountains, deserts, and forests, can offer unique
experiences for nature enthusiasts.
Somalia Background
Ancient Egyptians knew the area of present day Somalia as Punt.
The kingdom of Aksum occupied much of the area until Arab tribes settled along the Gulf of Aden coast, in the 7th century, and established the sultanate of Adel; around the port of Zeila.
The Somali people moved into the region from Yemen in the 13th century, and slowly the Somali chiefs ruled over small independent states within the disintegrating sultanate.
In 1839 Great Britain took possession of Aden, now in the Republic of Yemen, to provide safe anchorage for ships trading around the Arabian coast.
Italy developed an interest in the Somali coast during the late 19th century, and made treaties with local Somali sultans, and conventions with Great Britain, Ethiopia, and Zanzibar, to acquire outposts along the Indian Ocean.
Somalia was granted independence on July 1, 1960; merging with the former British protectorate of Somaliland which had become independent on June 26.
Military coups and civil wars followed; severely disrupting Somalia's infrastructure in the 1990s.
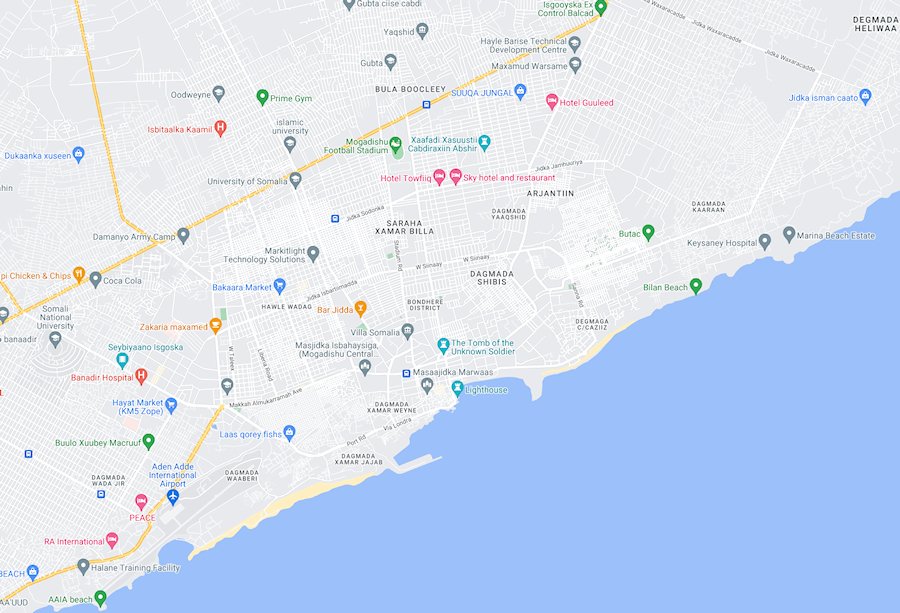
Mogadishu
Map of Mogadishu
Also called Muqdisho the country's capital, since independence in 1960, is in south-east Somalia; on the Indian Ocean, just north of the equator.
Mogadishu was founded by Arab merchants around the early 10th century, and it grew to become an important trading port.
The city came under the control of the sultan of Zanzibar in 1871.
The National Museum is in Mogadishu's Garesa Palace; built by the sultan of Zanzibar in the late 19th century.
Also visit the 13th-century mosque.
Hargeysa
Hargeysa, in northern Somalia, was a summer capital of the former British Somaliland, and the official capital from 1941 to 1960.
Kismaayo
Kismaayo, in southern Somalia, was founded in 1872 as a trade centre; by the sultan of Zanzibar.
The Sultan's former palace still stands and there are several mosques in Kismaayo worth visiting.
Somalia Maps and Travel Guides
Somalia Travel - Somalia Maps.
Weather in Africa:
Local weather forecasts for destinations around Africa.
More From Travel Notes
Travel Notes Online Guide to Travel
Africa - Asia - Caribbean - Europe - Middle East - North America - Oceania - South America.
The Travel Notes Online Guide to Travel helps visitors plan their trip with country and city travel guides, local tourist information, reviewed web sites, and inspiring travel content.
Travel and Tourism Guides on Travel Notes
If Travel Notes has helped you, please take a moment to like us on Facebook and share with your friends on social media.
Travel Resources
.
Travel & Tourism With Industry Professionals.